Porter’s Five Forces Forces Model is a framework for understanding the competitive forces at work in an industry. The model was developed by Michael Porter through the article ‘How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy’. The five forces are competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, supplier bargaining power, customer bargaining power, and threat of substitutes.
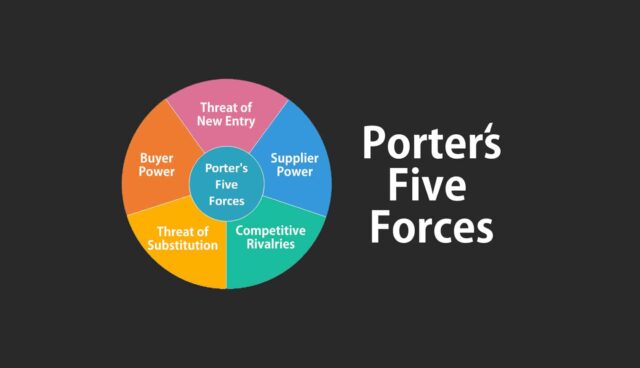
Competitive rivalry looks at the number and strength of your competitors. Competitive rivalry considers the number of rivals a business havs and the quality of their product compared with the company’s. Companies operating in industry where rivalry is intense attract customers by cutting prices and through marketing campaigns.
Suppliers are considered powerful if they can increase their prices easily, or reduce the quality of their product. Also, they are powerful when they are the only source of something important that a firm needs, can differentiate their product, or have strong brands. The more suppliers a company has to choose from, the easier it is to switch to a cheaper alternative. Fewer suppliers cause a company to rely heavily on them and gain a strong position.
Buyer power is when the number of buyers is low compared to the number of suppliers in an industry. Buyer power makes it easy for them to switch to new, cheaper competitors, which can ultimately drive down prices. Buyer power decreases when there are many customers and little competition.
The threat of substitutes is when customers find a different way of doing what the company does. The threat of substitution rises when customers find it easy to switch to another product, or when a new product enters the market.
A company’s position can be affected by potential rivals’ ability to enter your market. High costs required to switch between one supplier and another is a significant barrier to entry. APA
